6 Health Benefits Of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Health professionals have devoted considerable attention to omega-3 fatty acids on account of their numerous prospective health benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids are currently the subject of investigation due to their potential utility in the treatment of various ailments such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, dementia, and melancholy. In addition to supplements, omega-3 fatty acids are naturally present in a variety of foods, such as fatty salmon, nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables.
This article examines in greater detail several benefits of omega 3 fatty acids that have been supported by experts, as well as strategies for increasing your intake.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are present in numerous foods and supplements as a form of polyunsaturated fat. Omega 3 fatty acids are constituents of cellular membranes and modify cell receptors, thereby influencing a vast array of physiological processes, including the regulation of blood clotting and the reduction of inflammation. They are essential for the good health of the lungs, heart, brain, and blood vessels, among other organs and are linked to a variety of health benefits.
Read More: Top 10 Tips for Healthy Winter Skin
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids found in different food sources:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Omega-3 fatty acids are regarded as vital nutrients due to their inability to be produced endogenously by the body; therefore, they must be acquired through dietary sources or supplements, explains Cheryl Mussatto, a registered dietitian and author of The Nourished Brain based in Topeka, Kansas.
Food and Supplement Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
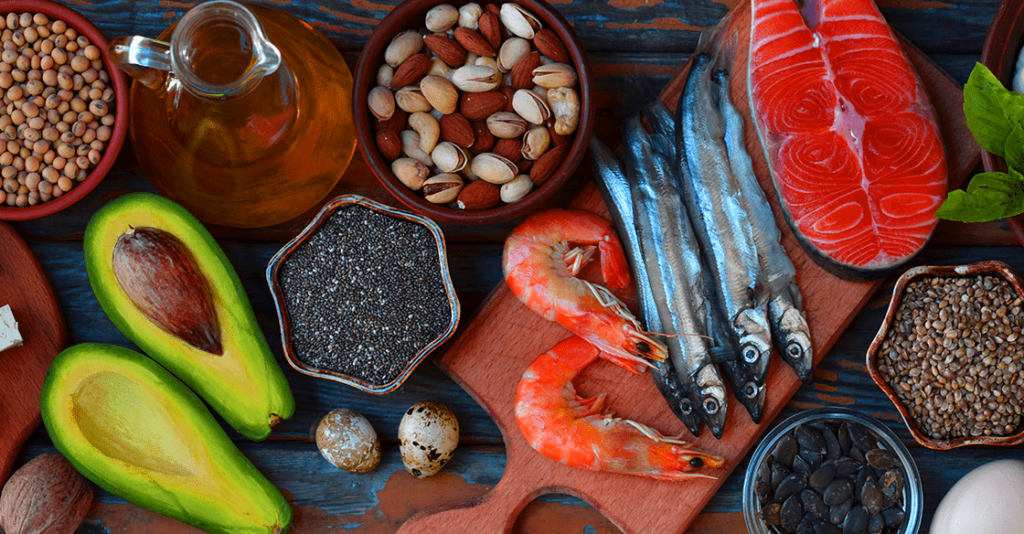

Salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and other oily fish varieties are particularly abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, such as DHA and EPA. Additionally available are plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as almonds, seeds, and vegetable oils. However, bear in mind that these foods contain ALA, which has a limited capacity for conversion to DHA and EPA.
Additionally, supplementation may be prudent to contemplate, particularly in cases where seafood is not a habitual component of one’s diet or when dietary sources prove insufficient to fulfill one’s requirements. Common supplements that contain omega-3 fatty acids include:
- Fish oil
- Fish liver oil
- Krill oil
- Algal oils
- Flaxseed oil
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The experimental findings regarding the potential advantages of omega-3 fatty acids are encouraging. Below, we examine several of the most significant health benefits associated with increasing your omega-3 intake.
Supports Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids have been the subject of extensive research due to their potential to protect against cardiac disease and maintain heart health. Mussatto explains that omega-3 fatty acids may benefit multiple facets of heart health by decreasing triglyceride levels, decreasing the risk of arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat), and delaying the accumulation of arterial plaque.
Indeed, an analysis of 38 studies revealed that omega-3 fatty acids may enhance outcomes for heart conditions, such as heart attack, and reduce the risk of death from heart disease. Fish oil supplementation significantly decreased the incidence of heart attack and cardiovascular disease, according to another study.
Promotes Prenatal Growth and Development
During pregnancy, omega-3 fatty acids are particularly vital, according to Hannah Whittaker, a registered dietitian based in Liverpool, United Kingdom, who specializes in pediatric and prenatal nutrition. She states, “Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically DHA, are vital for the development of the eyes and brains of infants.” There is a correlation between sufficient consumption of omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy and enhanced visual acuity and cognitive function in neonates.
Additionally, Whittaker explains that consuming sufficient omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial to maternal health during pregnancy. Indeed, research indicates that EPA reduces the risk of postpartum depression and alleviates symptoms of depression .Although research is inconsistent, some studies also indicate that omega-3s may reduce the risk of preterm birth.
Eases Inflammation
Whittaker adds, “Omega-3s also possess anti-inflammatory properties that may aid in the reduction of inflammation in the body.” A protracted list of health conditions, including obesity, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, may be exacerbated by chronic inflammation.
Omega-3 fatty acids may reduce levels of c-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammatory marker, in cancer patients, according to one meta-analysis . In adults with a variety of health conditions, omega-3 supplementation may reduce CRP and other inflammatory markers, according to the findings of a second comprehensive study .
May Improve Mental Health
“Omega-3 [fatty acids] may also be beneficial for mental health, according to research,” says Whittaker, adding that supplementation may help alleviate depressive and anxious symptoms. Omega-3 supplementation at both high and moderate doses was effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder when compared to a placebo, according to one study. An additional study demonstrated that omega-3 fatty acids may also alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Researchers hypothesize that omega-3 fatty acids function by altering neural pathways that modulate emotion and are implicated in the pathogenesis of specific psychiatric disorders. Omega-3 fatty acids have also been investigated as potential treatments for schizophrenia, mood disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and autism, although further research is required.
Enhances Brain Function
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for the regulation of brain function. According to Mussatto, they aid in cellular protection against oxidative stress, which may play a role in the pathogenesis of diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. According to a 2018 review published in Nutritional Neuroscience, omega-3 fatty acids may be particularly advantageous during the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, when there is a mild decline in brain function.
Several studies indicate that omega-3 fatty acids may also aid in the maintenance of cognitive function as one ages. Omega-3 fatty acids may have a positive effect on specific aspects of cognitive function in older individuals, including executive function, perceptual speed, and short-term memory, according to a review of fourteen studies [9]. Furthermore, an additional investigation reached the consensus that omega-3 fatty acids may enhance cerebral blood circulation, learning, memory, and cognitive health.
Supports Joint Health
Whittaker states, “Omega-3 fatty acids may assist individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory joint conditions in reducing joint pain and stiffness.” This could potentially be attributed to their anti-inflammatory characteristics and capacity to reduce the body’s synthesis of pro-inflammatory proteins.
When to See a Doctor
Mussatto states, “At this time, there is no standardized test for omega-3 deficiency, which makes it difficult to detect or pinpoint.” Nevertheless, specific symptoms may suggest a deficiency and warrant a consultation with a medical professional.
According to Mussatto, some of the key symptoms to keep an eye out for include:
- Thinning or brittle hair
- Skin problems, including rashes, irritation or acne
- Brain fog
- Joint pain or stiffness
Before beginning supplementation, you should also consult a physician if you have any preexisting conditions or are currently taking other medications. This is particularly crucial if you are taking blood thinners, such as warfarin, as the risk of bleeding may be increased by excessive doses of omega-3s.










2 Comments